Contact Us : 800.874.5346 International: +1 352.375.0772

There is one type of question you must master to pass the CIA Exam: multiple-choice. While you’ve probably answered plenty of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) before, you can’t write off CIA exam questions; they can be more complicated than standard MCQs. The more you know about CIA MCQs, the better you’ll do on the exam. In this blog, we’ll discuss how many and what kind of MCQs are on the exam so you can be completely prepared to pass.
A quick introduction to the exam format will help set the scene for the CIA exam questions. We’ve organized some of the exam basics for you in the chart below.
| Part | Number of Questions | Total Testing Time |
| Part 1: Internal Audit Basics | 125 | 150 minutes |
| Part 2: Internal Audit Practice | 100 | 120 minutes |
| Part 3: Internal Audit Knowledge Elements | 100 | 120 minutes |
There are five different types of CIA exam MCQs, but at the most basic level, each question consists of three parts:
You could see any combination of the five different MCQ types when you sit for each exam part. We’ll discuss each so you know what to expect.
1. An organization is in the process of establishing its new internal audit activity. The controller has no previous experience with internal auditors. Due to this lack of experience, the controller advised the applicants that the CAE will be reporting to the external auditors. However, the new chief audit executive will have free access to the controller to report anything important. The controller will then convey the CAE’s concerns to the board of directors. The internal audit activity will
Which of the following is not included in the statement of scope in an engagement final communication?
The purposes of the Standards include all of the following except
Presumably, The IIA will print negative words in bold, as we did here, but you should always read the question stem carefully and completely just in case. These questions can be tricky because they ask you to select the false answer choice among three correct answers, which can feel counterintuitive. To avoid being caught off guard, always give the question stem your undivided attention.
2. Which of the following facts, by themselves, could contribute to a lack of independence of the internal audit activity?
I. The CEO accused the new auditor of not operating “in the best interests of the organization.”
II. The majority of audit committee members come from within the organization.
III. The internal audit activity’s charter has not been approved by the board.
A. I only.
B. II only.
C. II and III only.
D. I, II, and III.
Our candidates have informed us that this type of question is one of the most difficult to answer, so we’ve made a special Gleim instructional video reviewing the best approaches to multiple-answer MCQs. You can find this video in your Gleim CIA Review Course or at dev.teamgleim.com/CIAMCQHelp. The best strategy is to determine which sentences you’re sure are right or wrong and use them to eliminate answer choices. Read the entire question stem carefully. Even if you’re not certain about the right answer, you have high odds for making a correct educated guess.
3. Which of the following represents the best statement of responsibilities for risk management?
| Management | Internal Auditing | Board |
| A. Responsibility for risk | Oversight role | Advisory role |
| B. Oversight role | Responsibility for risk | Advisory role |
| C. Responsibility for risk | Advisory role | Oversight role |
| D. Oversight role | Advisory role | Responsibility for risk |
CIA candidates have confirmed that this type of question can also be quite difficult, but again, our CIA multiple-choice question video can help you ace it. Ruling out answers as you go through each column is a very efficient and effective approach. Consider the example above. If you can’t remember the responsibilities of Management and Internal Auditing but know the Board plays an oversight role, you can just pick C, and you’ll get the question right.
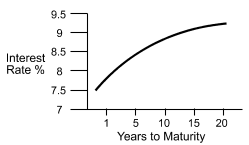
The yield curve shown implies that the
Most MCQs with visual elements are direct questions, but they may be one of the other question variations as well.
The CIA exam is computer-graded, so you receive your score right away. A passing score is 600, which corresponds to the minimum level of knowledge that CIAs need. The IIA determines your CIA exam score by calculating the number of questions answered correctly from the total number of questions on the exam and converting that number to a scale ranging from 250-750. If you earn at least a 600, your score report will simply say that you passed. If you didn’t score a 600, your score report will show your score as a number less than 600. You can then use this number to evaluate your passing performance.
You’ll get all the exposure to CIA exam questions you need by studying with the #1 CIA exam prep. Gleim CIA Review offers the best content coverage and the most refined test bank of MCQs available. Furthermore, our practice questions recreate the look, feel, and difficulty of the real CIA exam questions better than any other course on the market. See how well the best and most widely-used CIA review course will prepare you to pass by accessing our free CIA exam questions today!